Sciatica
Physiotherapy For Sciatica
Sciatica is one of the most common diagnoses that we see in physical therapy. But what exactly is sciatica and how do physical therapists treat this complex diagnosis? The simple answer is the treatment is all dictated by the source.
Generally, Sciatica is a term that is commonly used to describe pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling that radiates down the back of the leg. Typically, the symptoms follow the distribution of the sciatic nerve, but there can be some confusion as to the source of the pain especially when the patient’s symptoms are referred. Our job as PTs is to determine the source of the nerve irritation or referral origin and treat it accordingly with physiotherapy for sciatica. This is often accomplished with a thorough musculoskeletal exam and typically without the need for costly medical imaging. Below are the most common causes of sciatica seen in PT and how we typically treat them.
4 Types of Sciatica

Disc Herniation
The most common source of sciatica is pressure on the sciatic nerve from a herniation or protrusion of a spinal disc. This pressure on the nerve can create an irritation and inflammatory response causing symptoms to radiate down the leg following the path of the nerve that is compressed.
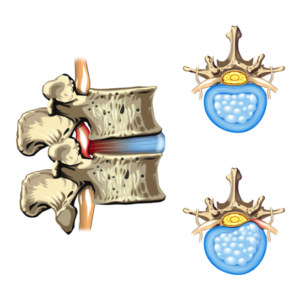
How Does Physical Therapy Help With Disc Herniation?
- Studies have shown that patients respond well to repetitive lumbar range of motion in improving sciatica symptoms related to lumbar disc herniation. Typically the direction that most patients report relief of their symptoms is lumbar extension. However, a thorough physiotherapy assessment will help decide a patient’s specific “directional preference”.
- Core stabilization exercises in conjunction with lumbar range of motion are also effective at reducing sciatica symptoms. PTs tend to focus on strengthening the transversus abdominis and gluteal muscles in both static and dynamic activities.
- Patient education is probably the most important component of the rehab of disc herniation. Patients are educated on proper sitting and standing postures as well as proper body mechanics with lifting activities to avoid causing further disc herniation.
Stenosis
Narrowing of the space where the spinal cord or nerve roots exit the spinal canal is called stenosis. If the space is narrowed, that can create pressure on the cord or the nerves causing pain to radiate down the leg.
Stenosis is typically seen in a condition called degenerative disc disease. Our discs are located between the bony vertebrates and over time they can start to lose some of their height. This loss of height causes the narrowing of space seen in stenosis.
Another cause of stenosis is tiny little bone spurs called osteophytes that can form in the spinal cord or nerve root space.
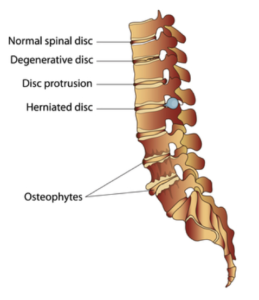
How Does Physical Therapy Help With Stenosis?
- Our goal in PT is typically to help improve ROM in the lumbar spine to help open up the narrowed space. Patients with stenosis often respond well to lumbar flexion or bending exercises, which is in contrast to the lumbar extension exercises often seen in disc herniation. However, a thorough physiotherapy exam will help determine the appropriate stretches/range of motion exercises.
- As with disc herniation, core stabilization and posture/movement retraining are important for patients with sciatica caused by stenosis.
- Functional dry needling (i.e. Trigger point dry needling) is also a very effective sciatica treatment. By using tiny, hair thin needles, we can quickly decrease the muscle tightness of spinal muscles, resulting in decreased compression of the lumbar vertebrae. We will discuss dry needling more in the last section.
Piriformis Syndrome
Deep in your buttock/gluts is a muscle that runs diagonally from the outside of your hip to the lowest part of your spine. This muscle, called the piriformis, can get short and tight or even be in spasm. In 85% of the population, the sciatic nerve runs just beneath the piriformis and in the other 15% it runs through the muscle. The sciatic nerve can become compressed and irritated when the piriformis is taught or in spasm creating symptoms of sciatica down the back of the leg.
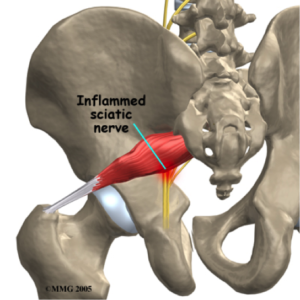
How Does Physical Therapy Help With Piriformis Syndrome?
- Typically, a physical therapist will prescribe a thorough home exercise program that includes stretches for the piriformis, hamstrings, and glute muscles (see linked video for example of a piriformis stretch).
- Sciatic nerve glides/flossing can be effective at getting the sciatic nerve moving again if it is trapped by the piriformis, especially in conjunction with the stretches above (see linked video for example of a sciatic nerve glide).
- A common theme with all of the causes of sciatica is core stabilization. Core and glute strengthening exercises will help to reduce the demands put on the piriformis muscle with daily and recreational activities (see linked video for an example of a core exercise).
Trigger Point Referral Pain
Trigger points are tender knots in skeletal muscles that often cause radiating or referral pain. In the case of sciatica, trigger points in the gluteus minimus, gluteus medius, and piriformis muscles are common sources of radiating pain into the back of the leg. Trigger points are located in almost all muscles in the body but usually lay dormant without referring pain. Dysfunction of movement patterns, compensation for weaknesses, or postural deficits, among many other things, can cause the trigger points in the dysfunctional muscle to become active and painful.
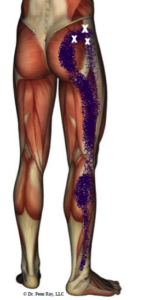
How Does Physical Therapy Help With Trigger Point Referral Pain?
- Physical therapists can assess movement patterns to determine if the trigger point is the source of sciatica symptoms and correct any movement dysfunction that they find.
- Joint mobilization, massage therapy, and myofascial release are common techniques to release or inhibit an active trigger point.
- Trigger point dry needling (also known as TDN, functional dry needling or intramuscular manual therapy) is becoming a very popular treatment for a variety of musculoskeletal issues but especially sciatica. As mentioned above, TDN involves the insertion of a tiny filiform needle into the trigger point. When the needle reaches the trigger point it creates a twitch response which feels like a cramp. The muscle relaxes and the trigger point becomes inhibited, alleviating the symptoms of sciatica.